Overview
Neural networks are one of the workhorses of machine learning. This is because the Universal Approximation Theorem gaurantees the ability of a neural network to approximate any function to an arbitrary degree of accuracy.
At a very basic level, a neural network is simply multiple layers of perceptrons stacked together.
Layer of Perceptrons
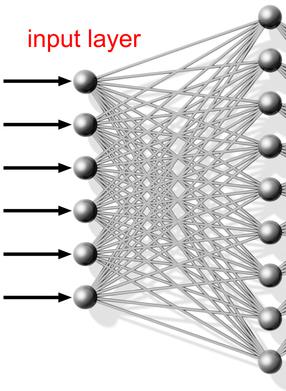
The first step to building a neural network is to create a set of perceptrons each of which has the same set of inputs.
The following is a depiction of 9 perceptrons, each with the same set of 6 inputs.
Activation Functions
The final step in the calculation of a perceptron is to pass the result through a step function. When perceptrons are used in a neural network, the function applied to the output of the weight multiplication is referred to as an activation function, and in general, is taken to be some function other than a step function.
In particular, the method of training a neural network requires the output of a layer to be differentiable (almost everywhere) , and to have some degree of non-linearity over the differentiable portions of the function. Because step functions fail this requirement, initial neural networks were intially designed to use sigmoid functions in place of the step function as the activation function.
As the theory was developed, other functions were tested and used as the activation function.
For more information, please see Activation Functions
Stacked Layers
The next step of building a neural network is to take the outputs of the layer of perceptrons (after passing through the activation function) and use those outputs as the inputs to another layer of perceptrons.
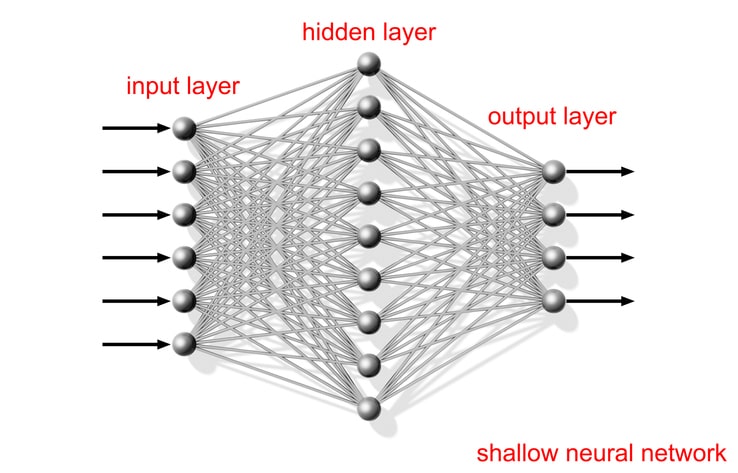
The initial desing of neural networks had only two layers, and in fact, the Universal Approxiation Theorem seems to indicate that that is all you need, however, there are benefits to creating deep neural networks (networks with more than two layers)
Topics
User Tracks
The following examples demonstrate using neural networks on some simple problems
Train a Machine Learning Algorithm for Digital Character Recognition
Uses tensor flow to create a neural network that is trained on a very simple representation of digit images.
start tensorflow
start javascript
Neural Network from Scratch
This example shows a very basic method to construct a simple neural network using a linear algebra library and
standard gradient descent.
start